
Within the cytoplasm, mitochondria are present in dispersed form. Axoplasm contains a cluster of microtubules and neurofilaments. This is due to the nodes of Ranvier over the myelin sheath.Īxoplasm: It makes up the axon’s empty portion or cytoplasmic material. It transmits electrical impulses all the way to axon terminals at a rapid rate.Note: Myelin contains protein and fatty substances that usually form around the brain and spinal cord nerves. Axons may or may not have a myelin sheath. Myelin sheath: is a multilamellar spiral of a cell membrane. Glia cells constitute the formation of the myelin sheath. Finally, they pass the synaptic inputs or nerve impulses to the soma.Īxolemma: It is a three-layered bi-lipid cell membrane that encircles the axon.Thus, dendrites provide a receptive surface for the synaptic inputs from the upstream neuron.


Transmission of the nerve impulse from axon to axon terminals involves the following stages: The cytoplasm of the axon hillock comprises neurofilaments that cluster into fascicles.

Group A and B are myelinated, and group C is nonmyelinated.Īxon originates from the initial segment or axon hillock that seems cone-like. Group A, B and C are the three types of axon. Multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain and spinal cord injury, peripheral neuropathies etc.Īutism, depression, anxiety, down syndrome etc.Īxons or nerve fibres are long and slender, located between soma and axon terminals. Malformations in neuron’s cytoplasmic projections It receives signals from the upstream neurons and passes to the cell body It transmits information from one neuron to the next via synapsis It originates from the conical axon hillockĪxon splits into fine branches (Telodendria)
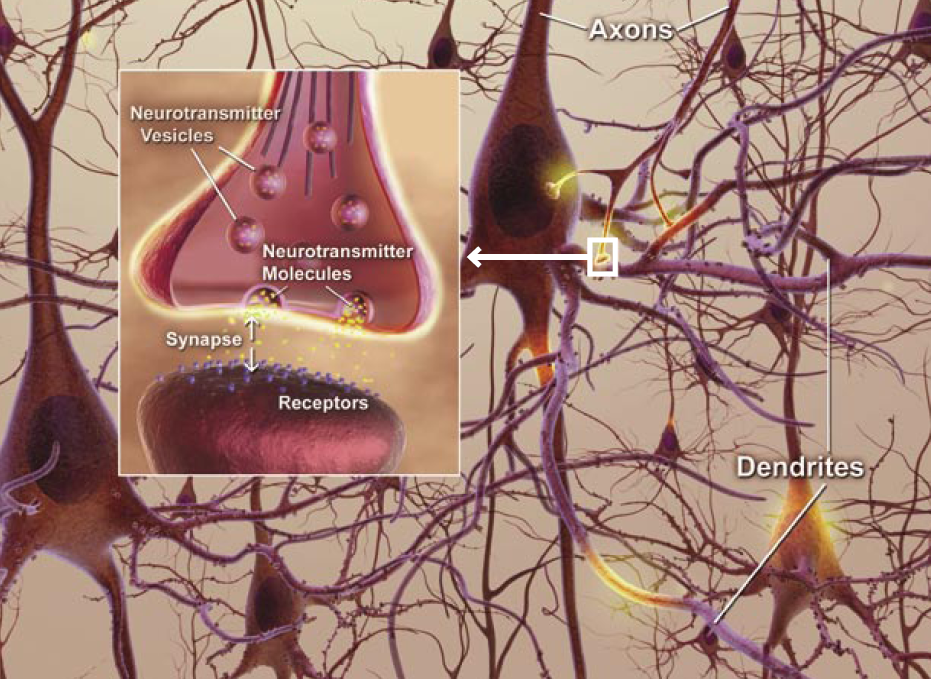
Variable (broad near the soma and taper at the end) Uniform (width is identical throughout the length) Neurons generally have one axon but may contain side branches or axon collateralsĪxons are relatively longer than the length of dendrites Content: Axon Vs DendriteĪxons are the cytoplasmic projections of the soma that appear as elongated fibresĭendrites are the cytoplasmic projection of the soma that appear as short branches Also, we will discuss the definition, comparison chart, structure and similarities between the two. This post describes the key differences between the axon and dendrite. Later, they propagate it throughout the cell body or soma. In contrast, dendrites receive the synaptic inputs from the axon terminal. They pass on information from one neuron to different neurons, muscles and glands. Length: Axons are long and their length may vary (one meter or more), while dendrites appear shorter in length.įunction: Axons perform a primary role in nerve impulse transmission. In contrast, dendrites often branch at semi-regular intervals. Branching: Axons tend to branch distally or sometimes may develop side branches.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
